7 Amazing Coconut water benefits that you did not know before
April 14, 2021“If you do not have control over your mouth, you will not have control over your future”. A lot of people in our country and even the whole world suffer from obesity. But what they do not realize is that obesity pulls them into a blackhole of diseases that ruins life after 40s. In fact, more people in the world die of diseases caused by obesity, than those who die from hunger. Therefore, obesity, if you have it, must be treated at any cost.
Deny it, or label it a lie, but deep down somewhere our inside makes us think about the effect of food that we are consuming on daily basis.
Whether that food is healthy or not, providing health benefits or not, we eat that to satisfy our cravings. Obesity is the major outcome of satisfying our cravings
In this article, we will discuss about obesity, its diagnosis, factors that influence it, and its consequences. At the end, we will discuss a few very effective tips which will help you lose weight.

WHAT IS OBESITY?
Obesity is a complex disease including an excessive amount of body fat. It arises owing to imbalance between total energy intake (food and beverages consumed) and total energy expenditure (energy used for work). Obesity isn’t just a cosmetic concern rather a medical dilemma that raises the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure and certain cancers.
PREDOMINANCE OF OBESITY:
- In United States, the prevalence of obesity was 19.3% and affected about 14.4 million children and adolescents. Obesity prevalence was 13.4% among 2- to 5-year-olds, 20.3% among 6- to 11-year-olds, and 21.2% among 12- to 19-year-olds.
- Pakistan has an estimated prevalence of childhood obesity between 15% to 20%. The proportion of obese and overweight children in Karachi was found to be 6% and 19% respectively.
DIAGNOSIS OF OBESITY:
Adults:
The most frequent detection is by weight to height ratio (BMI).
- BMI 25.0 to <30 : overweight
- BMI 30.0 or > 30: obese
Other methods for detection of fat free mass (FFM) are waist to hip ratio, waist circumference, mid upper arm circumference (MUAC), skinfold thickness and bioelectrical impedance.
Children:
Neck circumference (NC) is an affective screening method for obesity in children. The aims include:
- To assess the association between body mass index (BMI) and NC.
- To ascertain diagnostic performance involving the best cut-off values of NC for detection of overweight and obese children.
FACTORS INFLUENCING OBESITY:
Contributory factors are environmental changes, urbanization, lifestyles modification, high-density diets, less physical activity, medication. Behavior, environment, and genetic factors all have a role in obesity. Also, Food exposures, education and skills, food marketing and promotion, have resulted in rising burden of obesity. Positive family history, male gender, middle age, depression, carbonated drinks and fast food, overeating, and high calorie food intake too lead to obesity.
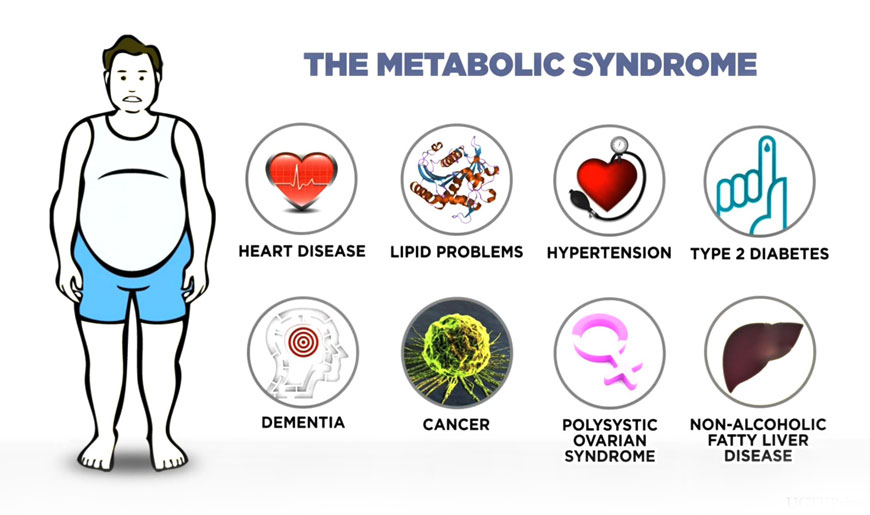
Consequences of obesity:
Health Consequences
Obese individuals are at heightened risk for critical health conditions, comprising:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High LDL cholesterol
- Low HDL cholesterol
- High levels of triglycerides (Dyslipidemia)
- Type 2 diabetes
- Coronary heart disease
- Stroke
- Gallbladder disease
- Osteoarthritis
- Sleep apnea and breathing complications
- Low quality of life
- Clinical depression & anxiety
- Body pain and difficulty with physical functioning
Economic and Societal Consequences
Obesity and accompanying health problems have a substantial economic influence on health care structure, involving direct and indirect costs. Direct medical costs incorporate preventive, diagnostic, and treatment facilities. Indirect costs correlate to sickness-death and involve lost productivity (employees absent for health reasons, diminished productivity while at work).
How to lose weight?

Obesity epidemic is a multifaceted dilemma and there must be a complex approach. Policy makers, organizations, businessmen, leaders, school, healthcare, and individuals must work collectively to generate a healthy lifestyle.
Healthy eating, being more physically active, and making other changes can help lose weight. People unable to lose enough weight are recommended weight-loss medicines, or bariatric surgery. Experts recommend losing 5 to 10 percent of body weight within the first 6 months of treatment.
- Following a low-calories healthy eating plan with regular physical activity is the first step to treat obesity.
- Developing coping skills that avert consuming food for emotional comfort, increasing self-efficacy regarding weight control, limiting screen-time, weight self-monitoring, and maintaining a consistent eating pattern.
- Doctor may prescribe medicines to treat severe obesity.
- Bariatric surgery includes several types of operations aiding weight-loss by making changes to digestive system. Bariatric surgery may be a preference in extreme obesity and stuck weight.
Dietary interventions
- Following low-fat, plant-based diets, grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits are low in fat and high in complex carbohydrates and fiber.
- Reducing dietary fat (Red-meats, dairy products, fried foods, and added oils).
- Choosing foods high in complex carbohydrates and fiber. whole grains and legumes provide fiber that is filling but contributes little to overall energy intake.
- Minimizing sugars (Sucrose, high-fructose corn syrup, and other simple sugars add calories without producing satiety).
- Skipping breakfast increases the risk of weight gain and obesity.
- When presented with larger portion, people tend to eat more, thus, portion sizes must be managed.
- More fruits and non-starchy vegetables consumption.
- Consumption of more fermented foods (such as Dahi and pickles).
- Enough protein (9 ounces per day such as of poultry, fish, eggs, chickpeas, beans, and lentils).
- Less quantity of fats (Oils and meat 0-2 servings)
- Moderate carbohydrates (less roti, chawal and wheat products)
- No processed foods
- Calorie-restricted diets: 1,200 to 1,500 calories/day for women and 1,500 to 1,800 calories/day for men. A lower calorie diet with a variety of healthy foods will give you the nutrients you need to stay healthy.
Conclusion:
All in all, health is a blessing, and we should not dig our graves with our teeth. In order to prevent obesity or to get rid of it, practice mindful eating, make physical exercise your routine, manage your sleep and stress, and stay away from all the processed and junk food.
This is a project of HND 5th semester, IFNS, PMAS Arid Agriculture University, Rawalpindi, headed by Mr. Tauseef Azam, under the course “Nutritional Education and Awareness”.


